Your Down Payment, Your Home's Key!
Apply NowWhat Should be the Down Payment?
We’ll say that your down payment for a $400,000 property is $20,000, or 5% of the total amount. Below is how much you should put down on a $800,000 house: Ten percent of the remaining $300,000 ($30,000) and 5% of the $500,000 ($25,000) make up the total down payment of $55,000.
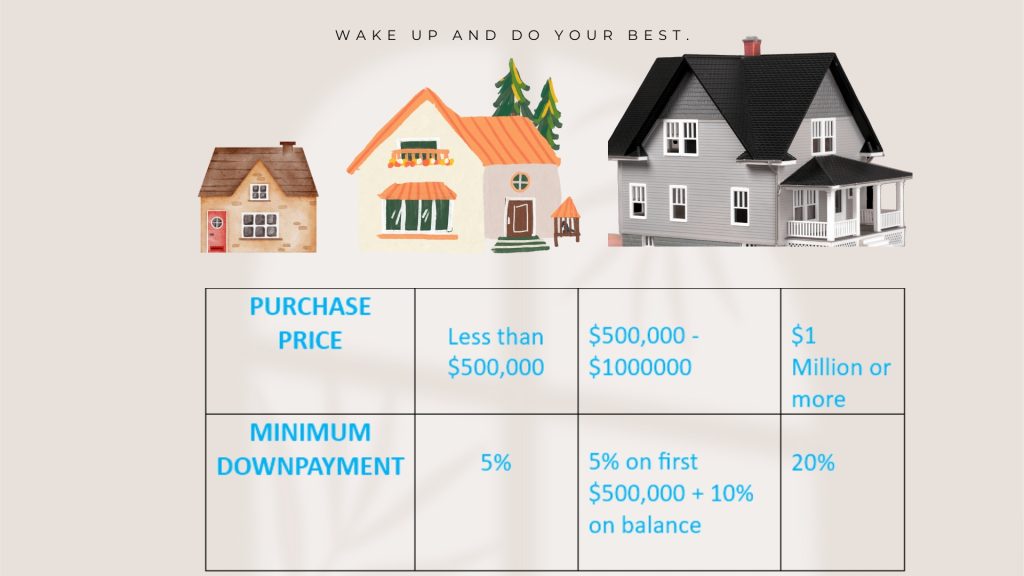
- Up to $500,000: A minimum down payment of 5% of the buying price is required for residences costing up to $500,000.
- Homes costing between $500,000 and $1,000,000: 10% of the remaining amount and 5% of the first $500,000 are the minimum down payments required for homes costing between $500,000 and $1,000,000.
- Homes costing more than $1 Million: A down payment of 20% of the buying price is required for homes above $1 million.
Potential homeowners in Canada are required to put down a deposit equal to a portion of the total cost of the property when making an offer to buy. A number of criteria, including the purchase price of the property, determine the precise down payment required to purchase a home in Canada. Long-term interest costs are also lowered with a larger down payment, in addition to monthly payment reductions. In addition, it reduces the requirement for a sizable credit amount in order to complete the transaction. Since it is the first out-of-pocket payment toward homeownership, this component has a big impact on the home-buying process. According to Canadian government laws, the minimum down payment required for real estate transactions is determined based on the price of the property.
Deposits can be made in many places:
- Individual savings: Opening a personal savings account is a common way to save money set aside for a down payment.
- Financial gifts: Receiving cash contributions from loved ones might also help you save money for a down payment.
- Property liquidation: You might get the money required for your down payment by selling your own property or other real estate holdings.
- Homebuyer initiatives: Acquiring cash for a down payment can be facilitated by a number of employer assistance programs and government initiatives in Canada.
The minimum down payment in Canada is divided into the following categories:
Benefits of larger down payments
If you can afford it, there are benefits to making a bigger down payment even if meeting the minimal criteria still allows you to purchase a property:
- Reduced monthly payments: Monthly payments that are lower Reduced monthly mortgage payments are the outcome of a greater initial payment, which also reduces the amount you should borrow.
- Decreased interest costs: Choosing a smaller mortgage results in less interest being paid overall.
- Exemption from mortgage default insurance: If your down payment surpasses 20%, there's no need for mortgage default insurance, translating to cost savings.
- Enhanced mortgage terms: For borrowers who make sizable down payments, lenders may provide more advantageous terms and interest rates.
Mortgage default insurance
Mortgage default insurance shields the lender in the event that a borrower doesn’t make a payment on schedule. You are required to obtain mortgage default insurance in cases where the down payment is less than twenty percent of the purchase price. A number of procedures are involved in calculating mortgage default insurance in Canada:
- Loan-to-Value Ratio(LTV): Division of the mortgage amount by the purchase price of the house yields this ratio.
- Determine the premium rate:
- Typically, the premium rate is around 4.00% for down payments ranging from 5% to 9.99% of the mortgage size.
- A premium rate of around 3.10% is common for down payments ranging from 10% to 14.99% of the mortgage amount.
- From 2.80% to 19.99% are typically the premium rates for down payments ranging from 15% to 19.99% of the total mortgage amount.
A down payment, the purchase price of the property, and the applicable premium rate are just a few of the details you’ll need to figure out the precise mortgage premium for your particular circumstances. Because every situation is different, your lender could offer you a premium rate.
- Compute the premium sum:
- In order to compute the precise premium amount, you must first ascertain the premium rate and the LTV ratio.
- How the premium amount is calculated is as follows: Total premium = Mortgage amount * Premium rate.
- You would pay $11,160 in premiums, for instance, if your mortgage was for $360,000 and your premium rate was 3.10%.
- Incorporate the premium into your mortgage principal:
- Although the mortgage premium is sometimes rolled into your mortgage principle, you won’t usually need to make a separate advance payment for it.
- As long as the premium is included in your mortgage, the total borrowing amount will include both the mortgage balance and the premium.
With smaller down payments in particular, mortgage default insurance can have a substantial effect on the total cost of homeownership. Because of this, it is essential that purchasers understand its intent. Once you have enough equity in your home, which frequently requires an assessment to ascertain the property’s current value and you may ask to have your mortgage insurance cancelled. All obligations to pay the insurance premium will end if the policy is terminated. Due diligence is advised on the part of borrowers, as premium prices and conditions for each mortgage insurance policy differ depending on the size of the down payment and the insurance provider selected. Crucially, these details might alter at any time and may vary depending on your finance institution’s practices and the terms of your mortgage agreement.
It basically means that the ideal down payment should be in line with your goals and financial situation, but it should also consider the advantages of making a larger initial investment. If you want to make an educated decision about the size of your down payment, it’s important to assess your individual financial circumstances carefully and consult with mortgage or financial experts.